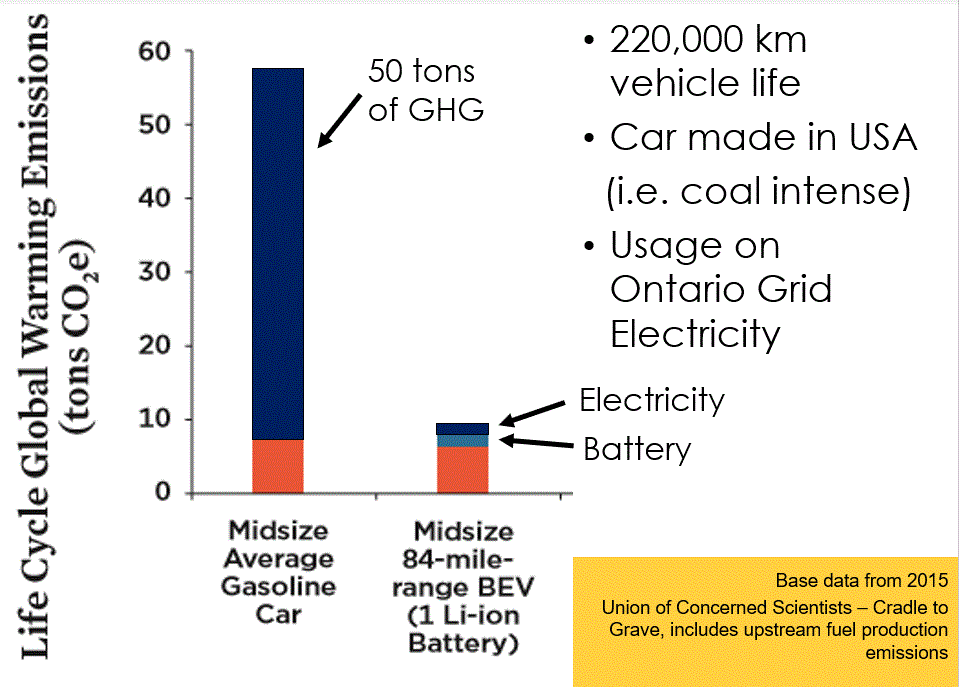
This chart shows the life cycle GHG emissions of an EV running on Ontario electricity. I took the data from a Union of Concerned Scientists study and modified it to use the GHG intensity of electricity made in Ontario to operate the EV. The bars show the life cycle emissions of a car made on the average US coal dominant electricity mix, but being driven in Ontario. Operating on low carbon Ontario electricity, the EV has life cycle GHG emissions about 1/5 that of the midsize gasoline car. This particular study analyzed an EV with a 150 km range and longer range EVs will have a larger light blue battery emissions contribution, but these emissions are still minimal compared to the GHG from the lifetime of gasoline GHG emissions (large dark blue baron the left). If the EV was made in a factory powered by low GHG intensity electricity, then the red GHG manufacturing emissions portion would also decrease. This would be the case for EVs made in Ontario. (S. Lapp)
Hydrogen as a fuel
Hydrogen is in the news, what are some of the basics of a hydrogen as a fuel.
Hydrogen…